paimon学习笔记
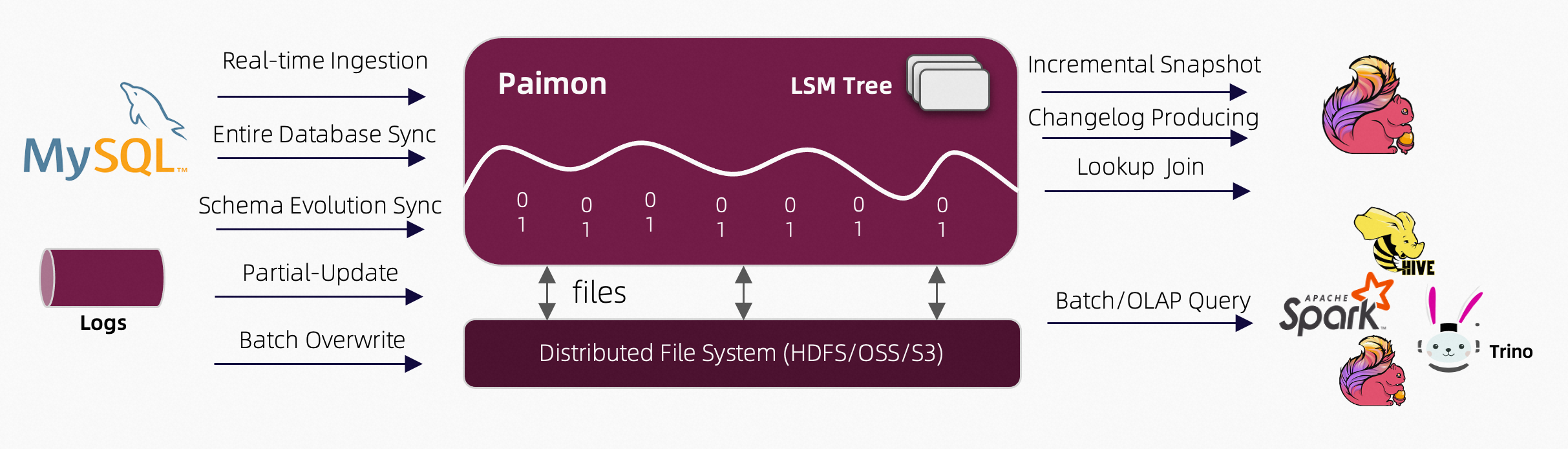
paimon架构
官方文档:https://paimon.apache.org/docs/1.0/concepts/overview/
1、创建paimon catalog
paimon catalog目前支持三种元数据存储,fs catalog:元数据和表数据存储在文件系统、hive catalog:元数据额外保存在hive metastore,支持hive访问表、jdbc catalog:元数据额外存储在mysql、postgresql等关系型数据库,前两者比较常用。paimon底层存储支持多种文件系统,例如本地文件系统,hadoop hdfs,阿里云oss,亚马逊s3等。
1.1、fs catalog
使用S3存储paimon表数据的话,需要下载依赖jar包放到flink下的lib目录,下载地址可以参考官方文档:https://paimon.apache.org/docs/1.0/maintenance/filesystems
测试中,我使用minio docker镜像搭建了S3对象存储服务,minio 与 Amazon S3 云存储服务 API 兼容。这里遇到2个问题,第一个是容器内部的时区问题,需要把时区调整到上海,可以通过添加环境变量TZ: Asia/Shanghai解决,第二个是s3.endpoint必须写ip,写hostname会超时连接不上。
-- 存储在hdfs
create catalog paimon_hdfs with (
'type' = 'paimon',
'warehouse' = 'hdfs://cluster1:8020/data/paimon/fs'
);
-- 存储在s3对象存储
create catalog paimon_s3 with (
'type' = 'paimon',
'warehouse' = 's3://data/paimon',
's3.endpoint' = 'http://192.168.8.200:9000',
's3.access-key' = 'xxx',
's3.secret-key' = 'xxx'
);1.2、hive catalog
使用hive catalog,需要下载依赖jar包放到flink下的lib目录,可以通过下面的链接下载,下面链接对应的hive版本是3.1.3,flink版本是1.20.2。
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-sql-connector-hive-3.1.3_2.12/1.20.2
遇到的问题:hive paimon的zstd-jni依赖冲突问题,导致使用hive查询paimon表时报错。paimon使用的zstd-jni版本为:1.5.5-11,hive3.1.3使用的zstd-jni版本为:1.3.2-2。使用下面第二个链接中的jar替换一下,查询报错问题就解决了。
https://github.com/apache/paimon/blob/release-1.0/pom.xml
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.luben/zstd-jni/1.5.5-11
create catalog paimon_hive with (
'type' = 'paimon',
-- 指定metastore为hive
'metastore' = 'hive',
-- 不设置的话,默认使用hive配置: hive.metastore.warehouse.dir目录
'warehouse' = 'hdfs://cluster1:8020/data/paimon/hive'
);1.3、jdbc catalog
create catalog paimon_jdbc with (
'type' = 'paimon',
'metastore' = 'jdbc',
'uri' = 'jdbc:postgresql://<host>:<port>/<databaseName>',
'jdbc.user' = '...',
'jdbc.password' = '...',
'catalog-key' = 'jdbc',
'warehouse' = 'hdfs://cluster1:8020/data/paimon/jdbc'
);2、创建paimon表
paimon支持下面的表类型:
- 主键表
- 非主键表/追加表
- 视图表
- 格式表:与hive兼容
- 对象表:(暂时不知道啥样的)
- 物化表
2.1、主键表
use catalog paimon_hdfs;
create database if not exists paimon_tutorial;
use paimon_tutorial;
create table user_table (
user_id string primary key not enforced,
name string,
age int
) with (
'bucket' = '1'
);2.2、非主键表
在batch模式下支持:DELETE、UPDATE、MERGE-INTO操作。
create table my_table (
a int,
b string
);2.3、视图表
需要catalog metastore支持。测试hive catalog支持,fs catalog和jdbc catalog不支持。不支持的话,只能使用临时视图,只在当前session有效。
create view if not exists my_table_view
(a, b)
as select a, b from my_table;
drop view if exists my_table_view;
show views;
show create view my_table_view;2.4、格式表
需要catalog metastore支持,hive catalog支持,hdfs catalog不支持,jdbc catalog没去测试。hdfs上表中的数据和hive表一致。没有paimon表中的schema、snapshot等数据。支持csv、orc、parquet格式数据。
use catalog paimon_hive;
create database if not exists paimon_test;
use paimon_test;
create table my_csv_table (
a int,
b string
) with (
'type' = 'format-table',
'file.format' = 'csv',
'field-delimiter' = ','
);
create table my_orc_table (
a int,
b string
) with (
'type' = 'format-table',
'file.format' = 'orc'
);
create table my_parquet_table (
a int,
b string
) with (
'type' = 'format-table',
'file.format' = 'parquet'
);2.5、对象表
用于存储非结构化数据,例如,图片、视频、音乐等文件。
create table `my_object_table` with (
'type' = 'object-table',
'object-location' = 'hdfs://cluster1:8020/data/object'
);
-- 刷新对象表
call sys.refresh_object_table('default.my_object_table');
-- 查询对象表
select * from my_object_table;
select * from my_object_table /*+ OPTIONS('scan.snapshot-id' = '1') */;对象表格式如下:
| name | type | null | key | extras | watermark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| path | STRING | FALSE | |||
| parent_path | STRING | FALSE | |||
| name | STRING | FALSE | |||
| length | BIGINT | FALSE | |||
| mtime | TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) | TRUE | |||
| atime | TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) | TRUE | |||
| owner | STRING | TRUE | |||
| generation | INT | TRUE | |||
| content_type | STRING | TRUE | |||
| storage_class | STRING | TRUE | |||
| md5_hash | STRING | TRUE | |||
| metadata_mtime | TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) | TRUE | |||
| metadata | MAP<STRING, STRING> | TRUE |
2.6、物化表
create materialized table continuous_users_shops
partitioned by (ds)
freshness = interval '30' second
as select
user_id,
ds,
sum (payment_amount_cents) as payed_buy_fee_sum,
sum (1) as pv
from (
select user_id, order_created_at as ds, payment_amount_cents
from json_source
) as tmp
group by user_id, ds;3、表元数据:系统表
系统表包含两种,数据系统表和全局系统表。数据系统表包含每个Paimon数据表的元数据和信息,例如创建的快照和使用的选项。
3.1、快照表:Snapshots Table
通过快照表,可以看出表的数据发生变化的次数。
select * from my_table$snapshots;3.2、Schemas Table
通过查询schemas table可以知道,表的schema历史变更。
select * from my_table$schemas;
-- 查询snapshot_id为3的数据schema信息
select
s.snapshot_id,
t.schema_id,
t.fields
from my_table$snapshots s
join my_table$schemas t
on s.schema_id = t.schema_id
where snapshot_id = 3;3.3、选项表:Options Table
表的配置信息
select * from my_table$options;3.4、日志审计表:Audit log Table
+I、-U、+U、-D
select * from my_table$audit_log;3.5、Binlog Table
有点类似上面的表,官方文档说,更新前更新后会合并到一行。
select * from pk_table$binlog;3.6、读优化表:Read-optimized Table
读写方式类似追加表
3.7、文件表:Files Table
select * from file_table$files /* OPTIONS('scan.snapshot-id'='3') */;3.8、Tags Table
select * from my_table$tags;3.9、Branches Table
select * from my_table$branches;3.10、消费者表:Consumers Table
消费者id以及要消费的下一个snapshot id
select * from my_table$consumers;3.11、Manifests Table
select * from my_table$manifests;3.12、Aggregation fields Table
后面学到聚合表,再看看这个。
select * from my_table$aggregation_fields;3.13、分区表:Partitions Table
select * from my_table$partitions;3.14、Buckets Table
select * from my_table$buckets;3.15、Statistic Table
select * from my_table$statistics;3.16、Table Indexes Table
select * from my_table$table_indexes;3.17、ALL Options Table(系统表)
hive catalog查询报错,另外两个查询正常。
use sys;
show tables;
select * from sys.all_table_options;3.18、Catalog Options Table(系统表)
select * from sys.catalog_options;4、主键表
定义表的时候可以使用主键,主键可以包含多个列,paimon强制在bucket中使用主键进行排序。
4.1、桶:bucket
无分区表和分区表分区下的数据,会再分成桶进行保存。每个bucket目录都包含一个LSM Tree和其变更日志。
bucket分桶由数据中一个或多个列的hash值决定,可以使用bucket-key选项定义决定bucket分桶的列。如果没有定义,主键表默认使用主键,非主键表使用整条数据。
bucket是用于读写的最小存储单元,因此bucket的数量限制了最大的处理并行度。bucket数量不应该太多,因为它会导致大量小文件和低读取性能。每个bucket中的推荐数据大小约为200MB-1GB。
4.1.1、固定分桶模式
通过’bucket’ = ’n’设置分桶数(n > 0),根据Math.abs(key_hashcode % numBuckets)计算数据属于哪个桶。
重新调整桶数,只能通过离线进程完成。桶的数量过多会导致小文件过多,桶的数量过少会导致写入性能问题。
4.1.2、动态分桶模式
主键表默认使用动态分桶,或者通过’bucket’ = ‘-1’设置。
- 选项1: ‘dynamic-bucket.target-row-num’: 一个bucket的数据条数
- 选项2: ‘dynamic-bucket.initial-buckets’: 初始bucket数量
仅支持单个写入任务。
- 普通动态分桶模式
- 当表没有分区,或者主键包含所有的分区字段。动态分桶模式使用HASH索引来维护从键到桶的映射,它比固定分桶模式需要更多的内存。1亿条数据多占用1G内存。普通动态桶模式支持排序压缩以加快查询速度。
- 跨分区动态分桶模式
- 主键没有包含所有的分区键字段。
- Deduplicate: 删除旧分区数据,新数据插入到新分区。
- PartialUpdate & Aggregation: 新数据插入到旧分区。
- FirstRow: 存在旧数据,则忽略新数据。
- 主键没有包含所有的分区键字段。
4.2、LSM Tree
Paimon采用LSM Tree (log-structured merge-tree)作为文件存储的数据结构。
4.3、表模式
4.3.1、Merge on read
MOR是主键表的默认模式。
优点:
- 写入性能很好。 缺点:
- 读取性能一般。
- 一个LSM Tree只能由一个线程读取,读取并行度受限。
- 当分桶数据量很大时,读取性能会非常低。bucket大小推荐200M-1G。
- 由于合并过程,不能对非主键列执行基于过滤器的数据跳过。
4.3.2、Copy on write
可以通过下面配置表模式为COW。COW模式每次写入都会进行合并操作,所有数据都将被合并到最新。读取时,不需要合并,读取性能最高。但每次写入都需要完全合并,写入放大非常严重。
ALTER TABLE orders SET ('full-compaction.delta-commits' = '1');优点:
- 读取性能很好。 缺点:
- 写入性能非常差。
4.3.3、Merge on write
可以通过下面配置表模式为MOW。由于Paimon的LSM结构,它能够通过主键进行查询。我们可以在写入时生成删除向量文件,表示文件中的哪些数据已被删除。这可以在读取过程中直接过滤掉不必要的行,这相当于合并,不会影响读取性能。
ALTER TABLE orders SET ('deletion-vectors.enabled' = 'true');优点:
- 读写性能都很好 缺点:
- 数据延迟问题(没看懂,后续探索一下)
4.3.4、MOR Read Optimized
后续用到再探索
4.4、合并引擎
当paimon主键表,接收到多条相同主键的数据时。paimon会将多条数据合并成一条,以保证主键的唯一性。合并引擎就是合并数据的方式。
deduplicate是默认的合并引擎,paimon会保存主键最新的数据,丢弃相同主键的旧数据。
partial-update: 部分列更新,为null的列,会被后面到来的非null数据更新,非null的列,会被后面到来非null的值更新。可以设计序列组,实现部分列一起更新(全非null才更新)
create table normal_merge_pu_tbl (
k int,
a int,
b int,
c int,
primary key (k) not enforced
) with (
'merge-engine' = 'partial-update'
);
insert into normal_merge_pu_tbl values (1, 23, 10, cast(null as int));
-- 查询时设置: set 'execution.runtime-mode' = 'batch';
select * from normal_merge_pu_tbl;
-- 1 | 23 | 10 | <NULL>
insert into normal_merge_pu_tbl values (1, cast(null as int), cast(null as int), 99);
select * from normal_merge_pu_tbl;
-- 1 | 23 | 10 | 99
insert into normal_merge_pu_tbl values (1, 25, 13, cast(null as int));
select * from normal_merge_pu_tbl;
-- 1 | 25 | 13 | 99